Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2025
- ICCV
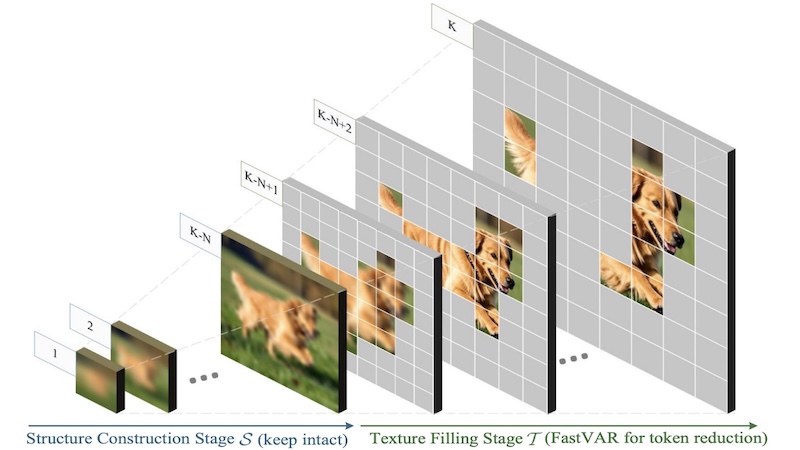 FastVAR: Linear Visual Autoregressive Modeling via Cached Token PruningHang Guo , Yawei Li , Taolin Zhang , and 4 more authorsThe IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025
FastVAR: Linear Visual Autoregressive Modeling via Cached Token PruningHang Guo , Yawei Li , Taolin Zhang , and 4 more authorsThe IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025Visual Autoregressive (VAR) modeling has gained popularity for its shift towards next-scale prediction. However, existing VAR paradigms process the entire token map at each scale step, leading to the complexity and runtime scaling dramatically with image resolution. To address this challenge, we propose FastVAR, a post-training acceleration method for efficient resolution scaling with VARs. Our key finding is that the majority of latency arises from the large-scale step where most tokens have already converged. Leveraging this observation, we develop the cached token pruning strategy that only forwards pivotal tokens for scale-specific modeling while using cached tokens from previous scale steps to restore the pruned slots. This significantly reduces the number of forwarded tokens and improves the efficiency at larger resolutions. Experiments show the proposed FastVAR can further speedup FlashAttention-accelerated VAR by 2.7 with negligible performance drop of <1%. We further extend FastVAR to zero-shot generation of higher resolution images. In particular, FastVAR can generate one 2K image with 15GB memory footprints in 1.5s on a single NVIDIA 3090 GPU. Code is available at https://github.com/csguoh/FastVAR.
@article{guo2025fastvar, title = {FastVAR: Linear Visual Autoregressive Modeling via Cached Token Pruning}, author = {Guo, Hang and Li, Yawei and Zhang, Taolin and Wang, Jiangshan and Dai, Tao and Xia, Shu-Tao and Benini, Luca}, journal = {The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)}, year = {2025}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/FastVAR}, } - CVPR
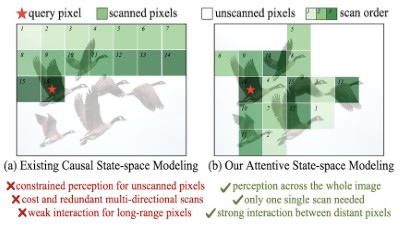 MambaIRv2: Attentive State Space RestorationHang Guo* , Yong Guo* , Yaohua Zha , and 5 more authorsThe IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025
MambaIRv2: Attentive State Space RestorationHang Guo* , Yong Guo* , Yaohua Zha , and 5 more authorsThe IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025The Mamba-based image restoration backbones have recently demonstrated significant potential in balancing global reception and computational efficiency. However, the inherent causal modeling limitation of Mamba, where each token depends solely on its predecessors in the scanned sequence, restricts the full utilization of pixels across the image and thus presents new challenges in image restoration. In this work, we propose MambaIRv2, which equips Mamba with the non-causal modeling ability similar to ViTs to reach the attentive state space restoration model. Specifically, the proposed attentive state-space equation allows to attend beyond the scanned sequence and facilitate image unfolding with just one single scan. Moreover, we further introduce a semantic-guided neighboring mechanism to encourage interaction between distant but similar pixels. Extensive experiments show our MambaIRv2 outperforms SRFormer by even 0.35dB PSNR for lightweight SR even with 9.3% less parameters and suppresses HAT on classic SR by up to 0.29dB.
@article{guo2024mambairv2, title = {MambaIRv2: Attentive State Space Restoration}, author = {Guo*, Hang and Guo*, Yong and Zha, Yaohua and Zhang, Yulun and Li, Wenbo and Dai, Tao and Xia, Shu-Tao and Li, Yawei}, journal = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}, year = {2025}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/MambaIR}, } - ICML
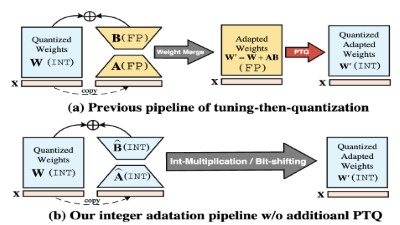 IntLoRA: Integral Low-rank Adaptation of Quantized Diffusion ModelsHang Guo , Yawei Li , Tao Dai , and 2 more authorsThe International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025
IntLoRA: Integral Low-rank Adaptation of Quantized Diffusion ModelsHang Guo , Yawei Li , Tao Dai , and 2 more authorsThe International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025Fine-tuning large-scale text-to-image diffusion models for various downstream tasks has yielded impressive results. However, the heavy computational burdens of tuning large models prevent personal customization. Recent advances have attempted to employ parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques to adapt the floating-point (FP) or quantized pre-trained weights. Nonetheless, the adaptation parameters in existing works are still restricted to FP arithmetic, hindering hardware-friendly acceleration. In this work, we propose IntLoRA, to further push the efficiency limits by using integer type (INT) low-rank parameters to adapt the quantized diffusion models. By working in the integer arithmetic, our IntLoRA offers three key advantages: (i) for fine-tuning, the pre-trained weights are quantized, reducing memory usage; (ii) for storage, both pre-trained and low-rank weights are in INT which consumes less disk space; (iii) for inference, IntLoRA weights can be naturally merged into quantized pre-trained weights through efficient integer multiplication or bit-shifting, eliminating additional post-training quantization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IntLoRA can achieve performance on par with or even superior to the vanilla LoRA, accompanied by significant efficiency improvements.
@article{guo2024intlora, title = {IntLoRA: Integral Low-rank Adaptation of Quantized Diffusion Models}, author = {Guo, Hang and Li, Yawei and Dai, Tao and Xia, Shu-Tao and Benini, Luca}, journal = {The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)}, year = {2025}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/IntLoRA}, } - AAAI
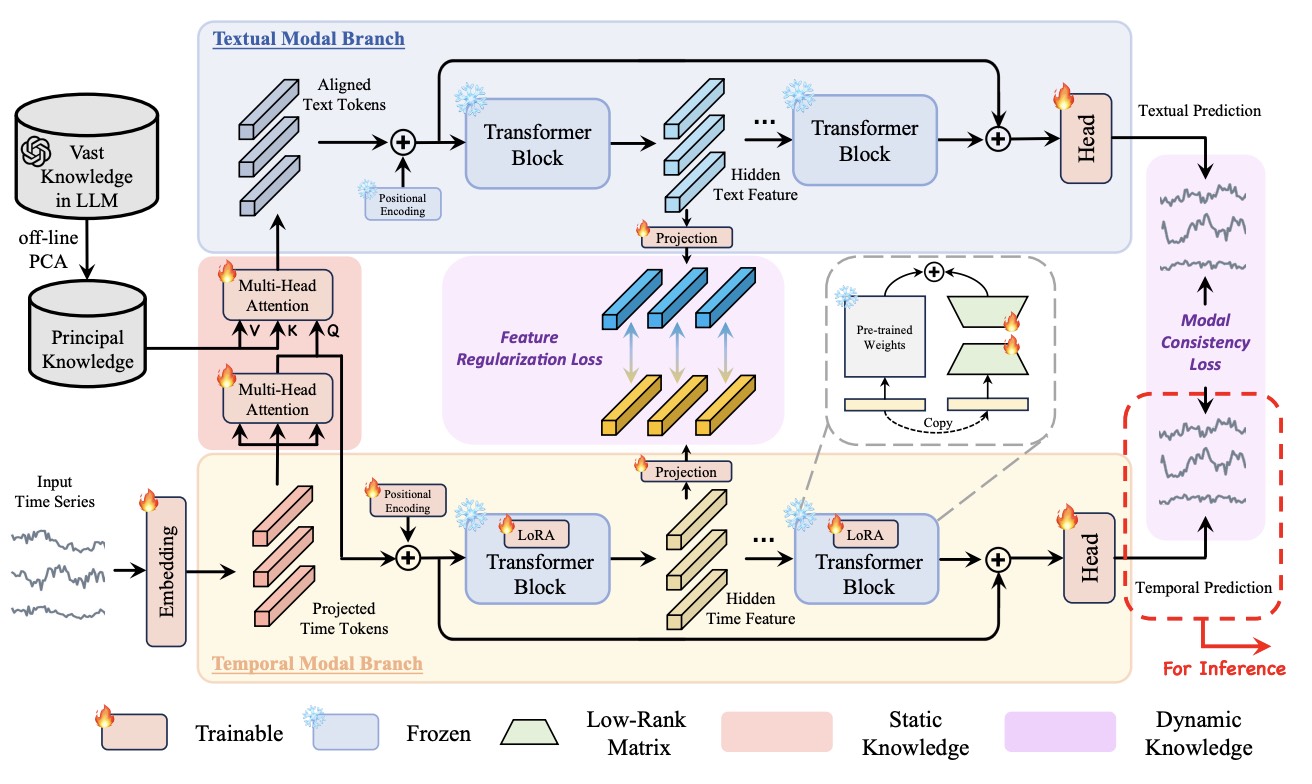 Taming Pre-trained LLMs for Generalised Time Series Forecasting via Cross-modal Knowledge DistillationPeiyuan Liu* , Hang Guo* , Tao Dai , and 5 more authorsAssociation for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2025
Taming Pre-trained LLMs for Generalised Time Series Forecasting via Cross-modal Knowledge DistillationPeiyuan Liu* , Hang Guo* , Tao Dai , and 5 more authorsAssociation for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2025@article{liu2024taming, title = {Taming Pre-trained LLMs for Generalised Time Series Forecasting via Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation}, author = {Liu*, Peiyuan and Guo*, Hang and Dai, Tao and Li, Naiqi and Bao, Jigang and Ren, Xudong and Jiang, Yong and Xia, Shu-Tao}, journal = {Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)}, year = {2025}, selected = true, repostar = {Hank0626/LLaTA}, }
2024
- NeurIPS
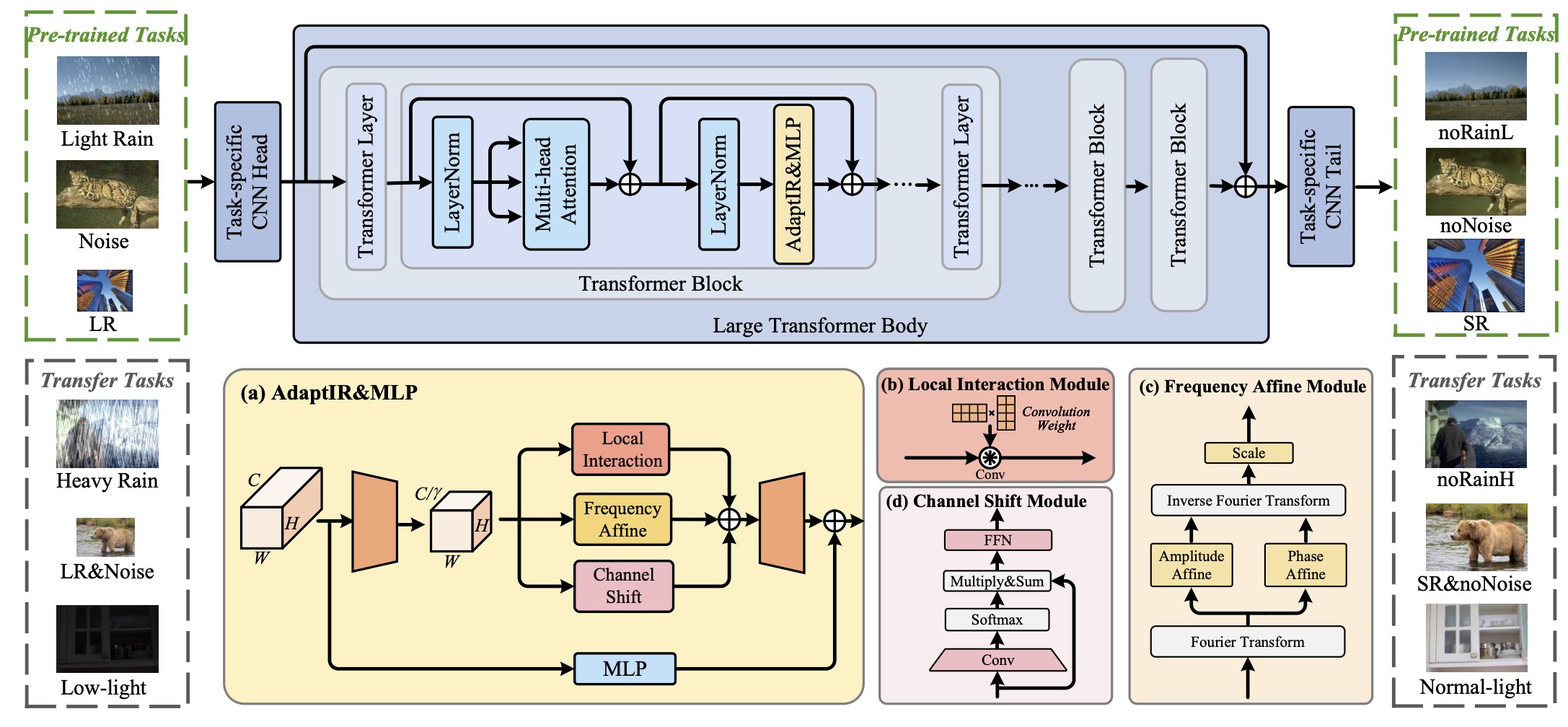 Parameter Efficient Adaptation for Image Restoration with Heterogeneous Mixture-of-ExpertsHang Guo , Tao Dai , Yuanchao Bai , and 4 more authorsThe Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024
Parameter Efficient Adaptation for Image Restoration with Heterogeneous Mixture-of-ExpertsHang Guo , Tao Dai , Yuanchao Bai , and 4 more authorsThe Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024Pre-training has shown promising results on various image restoration tasks, which is usually followed by full fine-tuning for each specific downstream task (e.g., image denoising). However, such full fine-tuning usually suffers from the problems of heavy computational cost in practice, due to the massive parameters of pre-trained restoration models, thus limiting its real-world applications. Recently, Parameter Efficient Transfer Learning (PETL) offers an efficient alternative solution to full fine-tuning, yet still faces great challenges for pre-trained image restoration models, due to the diversity of different degradations. To address these issues, we propose AdaptIR, a novel parameter efficient transfer learning method for adapting pre-trained restoration models. Specifically, the proposed method consists of a multi-branch inception structure to orthogonally capture local spatial, global spatial, and channel interactions. In this way, it allows powerful representations under a very low parameter budget. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve comparable or even better performance than full fine-tuning, while only using 0.6% parameters.
@article{guo2024adaptir, title = {Parameter Efficient Adaptation for Image Restoration with Heterogeneous Mixture-of-Experts}, author = {Guo, Hang and Dai, Tao and Bai, Yuanchao and Chen, Bin and Ren, Xudong and Zhu, Zexuan and Xia, Shu-Tao}, journal = {The Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)}, year = {2024}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/AdaptIR}, } - NeurIPS
 ReFIR: Grounding Large Restoration Models with Retrieval AugmentationHang Guo , Tao Dai , Zhihao Ouyang , and 4 more authorsThe Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024
ReFIR: Grounding Large Restoration Models with Retrieval AugmentationHang Guo , Tao Dai , Zhihao Ouyang , and 4 more authorsThe Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024Recent advances in diffusion-based Large Restoration Models (LRMs) have significantly improved photo-realistic image restoration by leveraging the internal knowledge embedded within model weights. However, existing LRMs often suffer from the hallucination dilemma, i.e., producing incorrect contents or textures when dealing with severe degradations, due to their heavy reliance on limited internal knowledge. In this paper, we propose an orthogonal solution called the Retrieval-augmented Framework for Image Restoration (ReFIR), which incorporates retrieved images as external knowledge to extend the knowledge boundary of existing LRMs in generating details faithful to the original scene. Specifically, we first introduce the nearest neighbor lookup to retrieve content-relevant high-quality images as reference, after which we propose the cross-image injection to modify existing LRMs to utilize high-quality textures from retrieved images. Thanks to the additional external knowledge, our ReFIR can well handle the hallucination challenge and facilitate faithfully results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReFIR can achieve not only high-fidelity but also realistic restoration results. Importantly, our ReFIR requires no training and is adaptable to various LRMs.
@article{guo2024refir, title = {ReFIR: Grounding Large Restoration Models with Retrieval Augmentation}, author = {Guo, Hang and Dai, Tao and Ouyang, Zhihao and Zhang, Taolin and Zha, Yaohua and Chen, Bin and Xia, Shu-Tao}, journal = {The Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)}, year = {2024}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/ReFIR}, } - ECCV
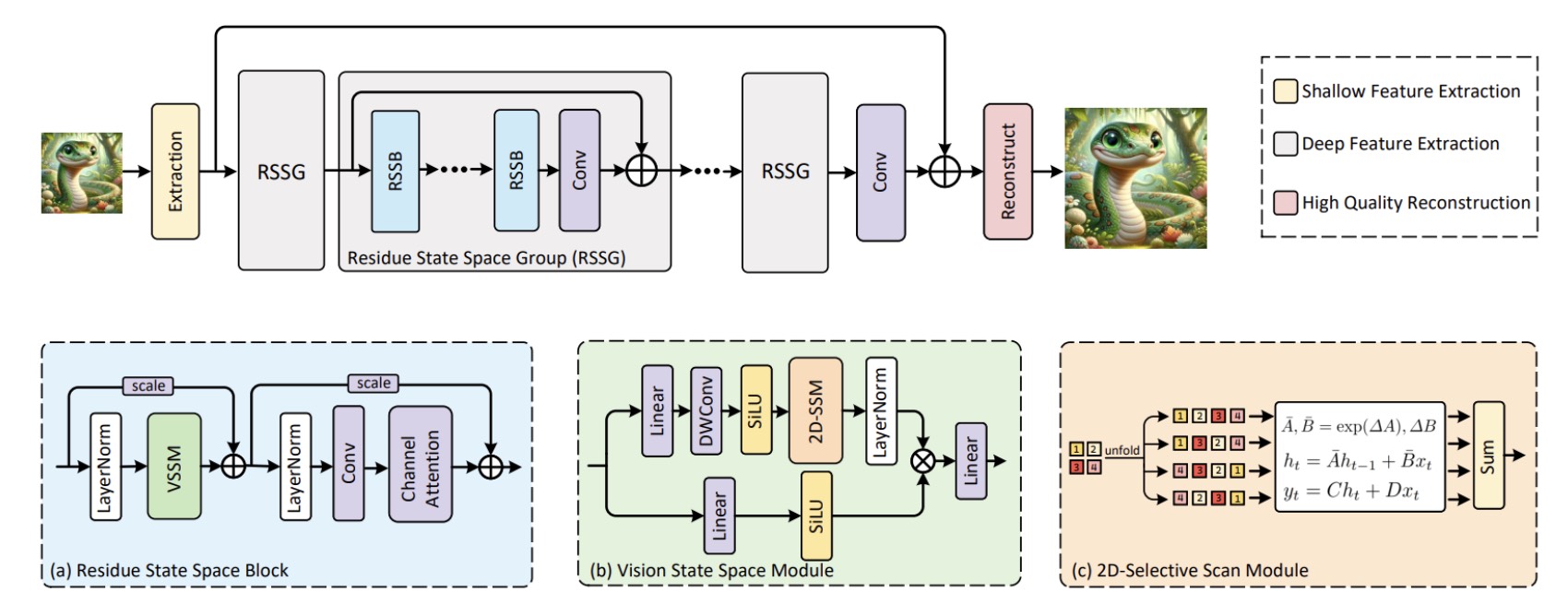 MambaIR: A Simple Baseline for Image Restoration with State-Space ModelHang Guo* , Jinmin Li* , Tao Dai , and 3 more authorsProceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024
MambaIR: A Simple Baseline for Image Restoration with State-Space ModelHang Guo* , Jinmin Li* , Tao Dai , and 3 more authorsProceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024Recent years have witnessed great progress in image restoration thanks to the advancements in modern deep neural networks e.g. Convolutional Neural Network and Transformer. However, existing restoration backbones are usually limited due to the inherent local reductive bias or quadratic computational complexity. Recently, Selective Structured State Space Model e.g., Mamba, have shown great potential for long-range dependencies modeling with linear complexity, but it is still under-explored in low-level computer vision. In this work, we introduce a simple but strong benchmark model, named MambaIR, for image restoration. In detail, we propose the Residual State Space Block as the core component, which employs convolution and channel attention to enhance capabilities of the vanilla Mamba. In this way, our MambaIR takes advantages of local patch recurrence prior as well as channel interaction to produce restoration-specific feature representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method, for example, MambaIR outperforms Transformer-based baseline SwinIR by up to 0.36dB, using similar computational cost but with global receptive field.
@article{guo2024mambair, title = {MambaIR: A Simple Baseline for Image Restoration with State-Space Model}, author = {Guo*, Hang and Li*, Jinmin and Dai, Tao and Ouyang, Zhihao and Ren, Xudong and Xia, Shu-Tao}, journal = {Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)}, year = {2024}, selected = true, repostar = {csguoh/MambaIR}, } - IJCAI
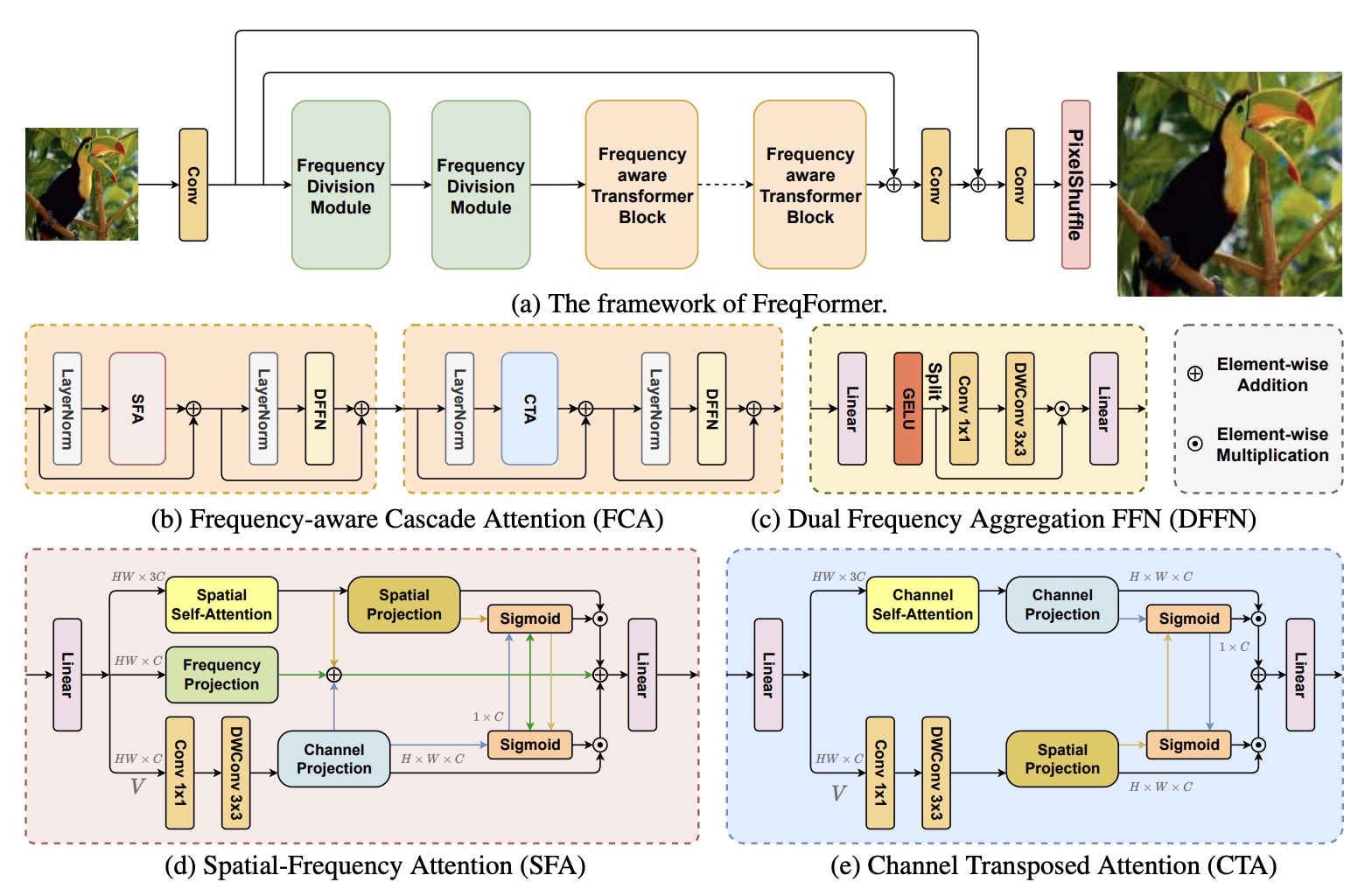 FreqFormer: Frequency-aware Transformer for Lightweight Image Super-resolutionTao Dai , Jianping Wang , Hang Guo , and 3 more authorsProceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2024
FreqFormer: Frequency-aware Transformer for Lightweight Image Super-resolutionTao Dai , Jianping Wang , Hang Guo , and 3 more authorsProceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2024Transformer-based models have been widely and successfully used in various low-vision visual tasks, and have achieved remarkable performance in single image super-resolution (SR). Despite the significant progress in SR, Transformer-based SR methods (e.g., SwinIR) still suffer from the problems of heavy computation cost and low-frequency preference, while ignoring the reconstruction of rich high-frequency information, hence hindering the representational power of Transformers. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose a novel Frequency-aware Transformer (FreqFormer) for lightweight image SR. Specifically, a Frequency Division Module (FDM) is first introduced to separately handle high- and low-frequency information in a divide-and-conquer manner. Moreover, we present Frequency-aware Transformer Block (FTB) to extracting both spatial frequency attention and channel transposed attention to recover high-frequency details. Extensive experimental results on public datasets demonstrate the superiority of our FreqFormer over state-of-the-art SR methods in terms of both quantitative metrics and visual quality.
@article{wang2024freqformer, title = {FreqFormer: Frequency-aware Transformer for Lightweight Image Super-resolution}, author = {Dai, Tao and Wang, Jianping and Guo, Hang and Li, Jinmin and Wang, Jinbao and Zhu, Zexuan}, journal = {Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI)}, year = {2024}, selected = false, }
2023
- IJCAI
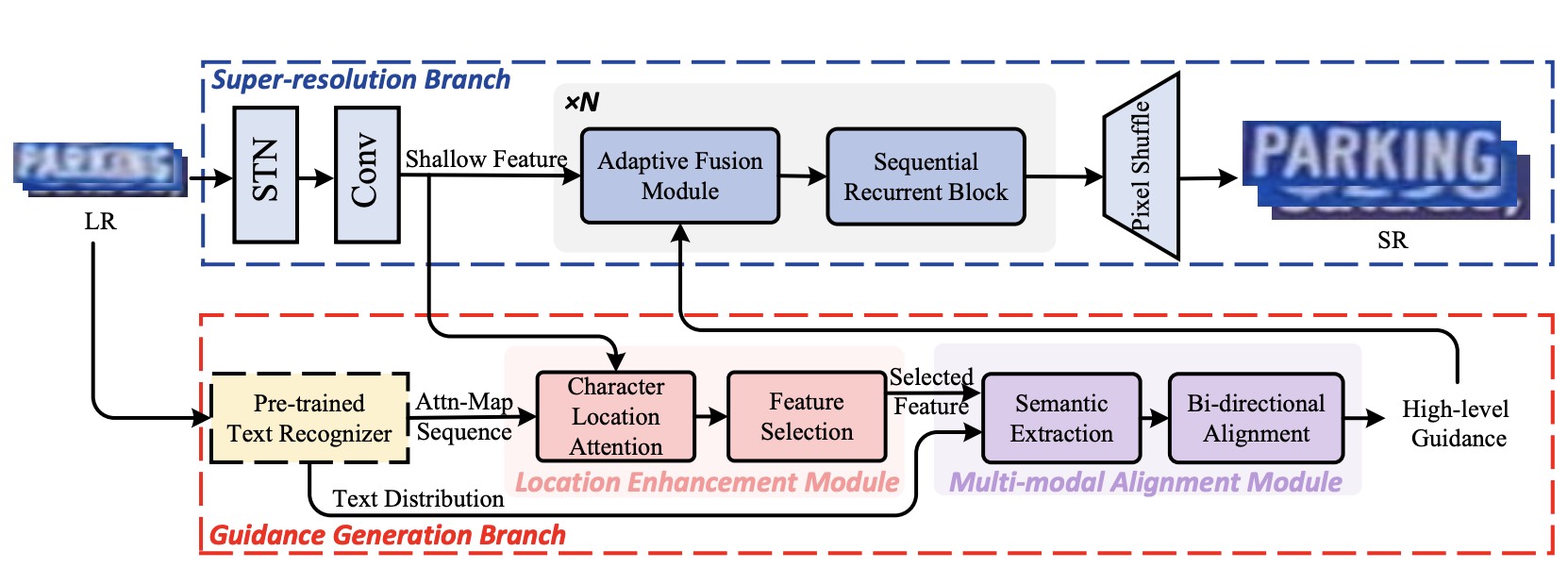 Towards Robust Scene Text Image Super-resolution via Explicit Location EnhancementHang Guo , Tao Dai , Guanghao Meng , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) , 2023
Towards Robust Scene Text Image Super-resolution via Explicit Location EnhancementHang Guo , Tao Dai , Guanghao Meng , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) , 2023Scene text image super-resolution (STISR), aiming to improve image quality while boosting downstream scene text recognition accuracy, has recently achieved great success. However, most existing methods treat the foreground (character regions) and background (non-character regions) equally in the forward process, and neglect the disturbance from the complex background, thus limiting the performance. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose a novel method LEMMA that explicitly models character regions to produce high-level text-specific guidance for super-resolution. To model the location of characters effectively, we propose the location enhancement module to extract character region features based on the attention map sequence. Besides, we propose the multi-modal alignment module to perform bidirectional visual-semantic alignment to generate high-quality prior guidance, which is then incorporated into the super-resolution branch in an adaptive manner using the proposed adaptive fusion module. Experiments on TextZoom and four scene text recognition benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our method over other state-of-the-art methods.
@inproceedings{guo2023lemma, title = {Towards Robust Scene Text Image Super-resolution via Explicit Location Enhancement}, author = {Guo, Hang and Dai, Tao and Meng, Guanghao and Xia, Shu-Tao}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI)}, publisher = {International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization}, pages = {782--790}, year = {2023}, repostar = {csguoh/LEMMA}, } - ACM MM
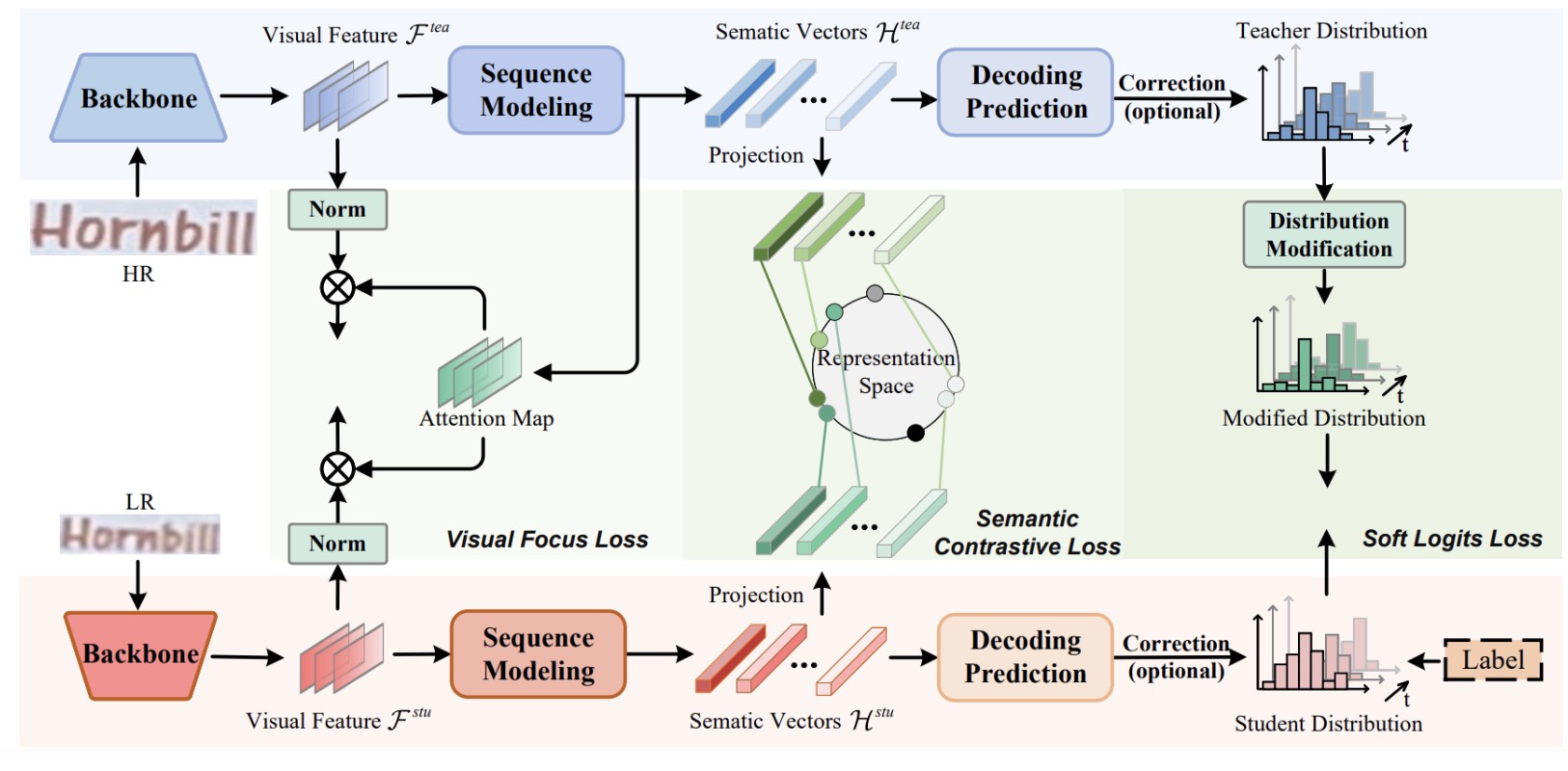 One-stage Low-resolution Text Recognition with High-resolution Knowledge TransferHang Guo , Tao Dai , Mingyan Zhu , and 4 more authorsIn Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM) , 2023
One-stage Low-resolution Text Recognition with High-resolution Knowledge TransferHang Guo , Tao Dai , Mingyan Zhu , and 4 more authorsIn Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM) , 2023Recognizing characters from low-resolution (LR) text images poses a significant challenge due to the information deficiency as well as the noise and blur in low-quality images. Current solutions for low-resolution text recognition (LTR) typically rely on a two-stage pipeline that involves super-resolution as the first stage followed by the second-stage recognition. Although this pipeline is straightforward and intuitive, it has to use an additional super-resolution network, which causes inefficiencies during training and testing. Moreover, the recognition accuracy of the second stage heavily depends on the reconstruction quality of the first stage, causing ineffectiveness.In this work, we attempt to address these challenges from a novel perspective: adapting the recognizer to low-resolution inputs by transferring the knowledge from the high-resolution. Guided by this idea, we propose an efficient and effective knowledge distillation framework to achieve multi-level knowledge transfer.Specifically, the visual focus loss is proposed to extract the character position knowledge with resolution gap reduction and character region focus, the semantic contrastive loss is employed to exploit the contextual semantic knowledge with contrastive learning, and the soft logits loss facilitates both local word-level and global sequence-level learning from the soft teacher label.Extensive experiments show that the proposed one-stage pipeline significantly outperforms super-resolution based two-stage frameworks in terms of effectiveness and efficiency, accompanied by favorable robustness.
@inproceedings{guo2023one, title = {One-stage Low-resolution Text Recognition with High-resolution Knowledge Transfer}, author = {Guo, Hang and Dai, Tao and Zhu, Mingyan and Meng, Guanghao and Chen, Bin and Wang, Zhi and Xia, Shu-Tao}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM)}, pages = {2189--2198}, year = {2023}, repostar = {csguoh/KD-LTR}, }
2022
- TCSVT
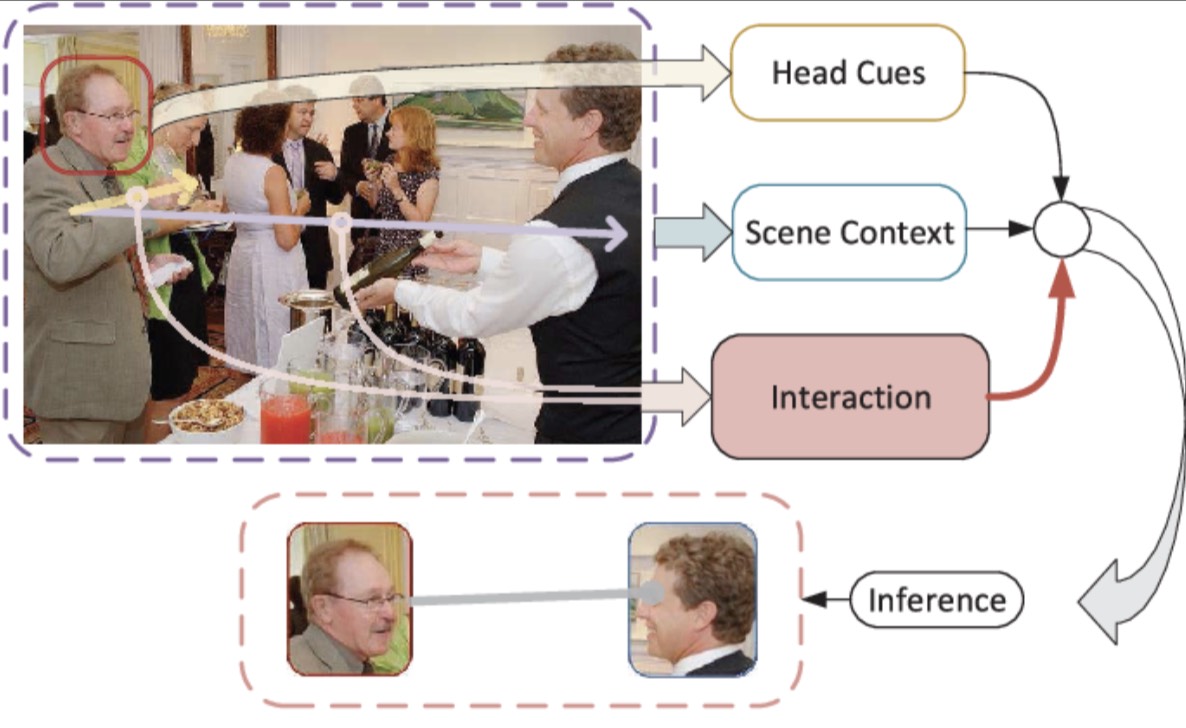 Gaze target estimation inspired by interactive attentionZhengxi Hu , Kunxu Zhao , Bohan Zhou , and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 2022
Gaze target estimation inspired by interactive attentionZhengxi Hu , Kunxu Zhao , Bohan Zhou , and 4 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 2022As an essential nonverbal cue, the human gaze reveals human intentions and plays a crucial role in human daily activities. Therefore, automatic detection of the person’s gaze target has drawn the interests of the computer vision community. This is useful not only for identifying whether children are attentive in class but also for locating items of interest to humans in retail settings. Existing gaze-following methods have only explored and exploited the scenes context and the head cues. Considering the significance of human-object interaction in understanding human intentions, we present the Visual-Spatial Graph and introduce a graph attention network to analyze the interaction probability between the human and elements in the scene. Then the interaction probability inferred from the visual-spatial information that is aggregated by the attention mechanism can be transformed into an interactive attention map that depicts the areas people care about. In addition, we construct a transformer as an encoder to integrate the features extracted by the scene and head pathways aiming to decode the gaze target. After introducing interactive attention, our proposed method achieves outstanding performance on two benchmarks: GazeFollow and VideoAttentionTarget.
@article{hu2022gaze, title = {Gaze target estimation inspired by interactive attention}, author = {Hu, Zhengxi and Zhao, Kunxu and Zhou, Bohan and Guo, Hang and Wu, Shichao and Yang, Yuxue and Liu, Jingtai}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)}, volume = {32}, number = {12}, pages = {8524--8536}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, } - ACCV
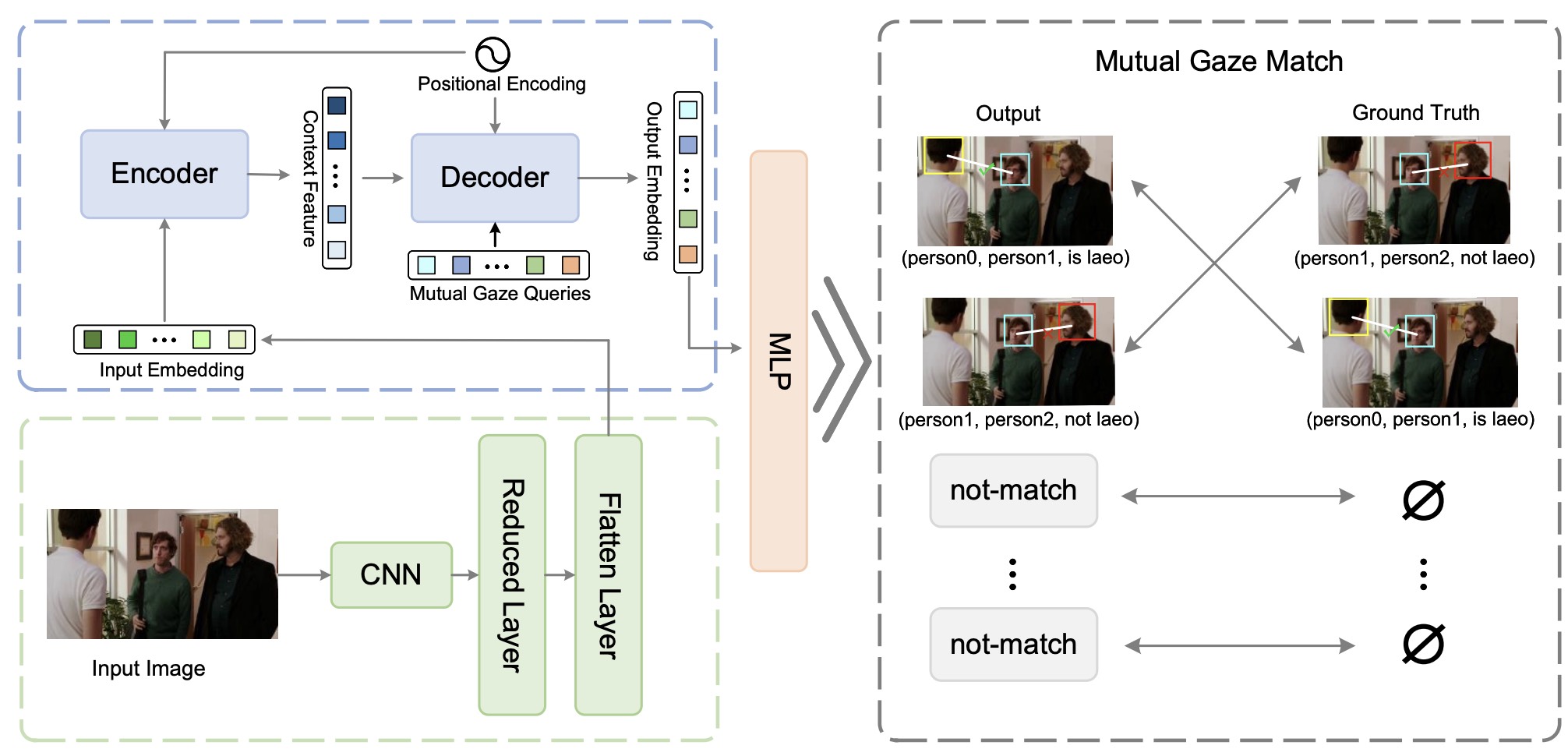 MGTR: End-to-End Mutual Gaze Detection with TransformerHang Guo , Zhengxi Hu , and Jingtai LiuIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) , 2022
MGTR: End-to-End Mutual Gaze Detection with TransformerHang Guo , Zhengxi Hu , and Jingtai LiuIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) , 2022People’s looking at each other or mutual gaze is ubiquitous in our daily interactions, and detecting mutual gaze is of great significance for understanding human social scenes. Current mutual gaze detection methods focus on two-stage methods, whose inference speed is limited by the two-stage pipeline and the performance in the second stage is affected by the first one. In this paper, we propose a novel one-stage mutual gaze detection framework called Mutual Gaze TRansformer or MGTR to perform mutual gaze detection in an end-to-end manner. By designing mutual gaze instance triples, MGTR can detect each human head bounding box and simultaneously infer mutual gaze relationship based on global image information, which streamlines the whole process with simplicity. Experimental results on two mutual gaze datasets show that our method is able to accelerate mutual gaze detection process without losing performance. Ablation study shows that different components of MGTR can capture different levels of semantic information in images.
@inproceedings{guo2022mgtr, title = {MGTR: End-to-End Mutual Gaze Detection with Transformer}, author = {Guo, Hang and Hu, Zhengxi and Liu, Jingtai}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV)}, pages = {1590--1605}, year = {2022}, repostar = {csguoh/MGTR}, }








